Marine Animals Definition Biology

Given that in biology many phyla families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy.
Marine animals definition biology. Spongin- flexible protein fibers. Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life organisms in the sea. Archaeocytes- cells that move through the sponge.
Collar cells- create moving force in a sponges body. A marine biologist is someone who is interested in learning and studying marine organisms and what their lives are like in their natural habitats. As a marine biologist you may study a wide range of topics from the behavior physiology and ecology of specific groups of organisms to the interactions between human activity and aquatic environments.
Our ocean coasts and estuaries are home to diverse living things. This type of pollution occurs when human activities notably the use of fertilizer on farms lead. Spicules- skeletal elements that support a sponge.
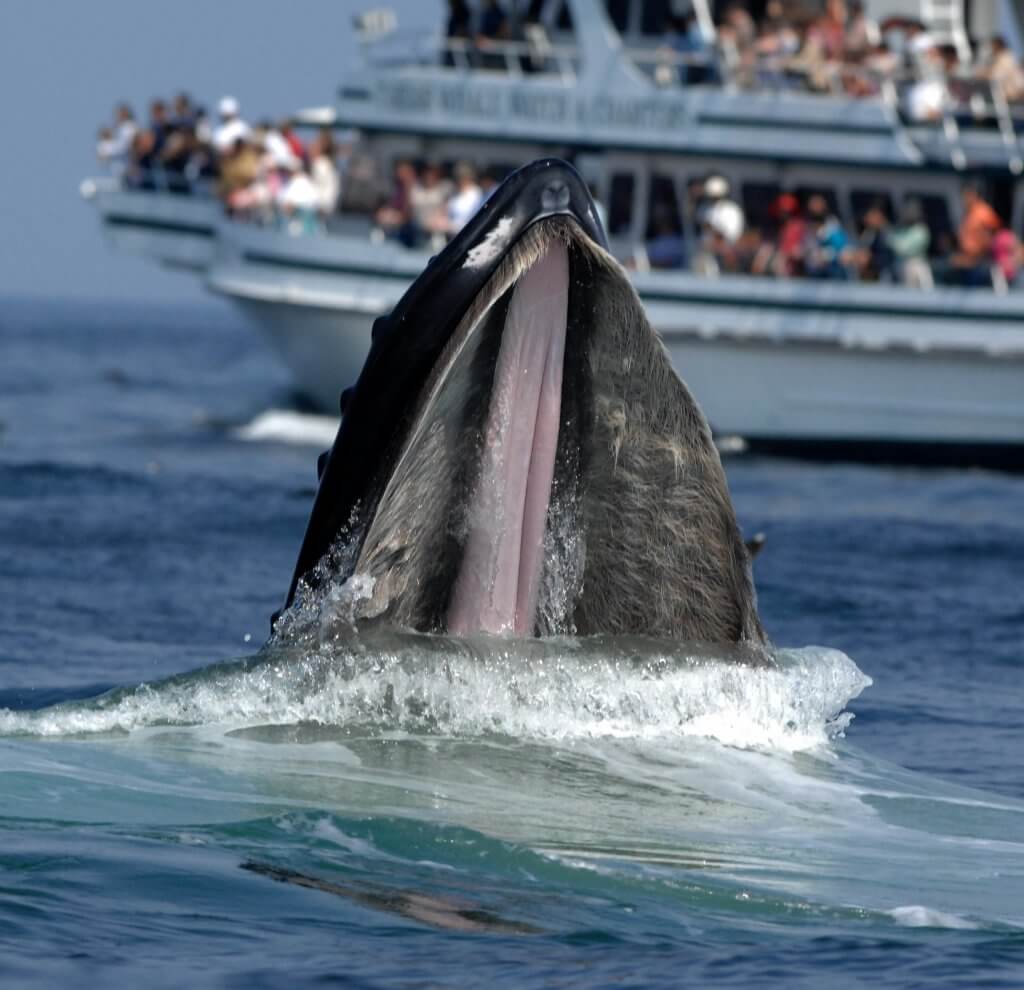
Marine biologists study a wide variety of aquatic organisms from microscopic plankton to massive whales. But marine biology is so much more than making a dolphin -- or sea lion -- follow commands. An animal belonging to the mammalian order Sirenia which includes manatees and dugongs.
When we talk about marine life the first thing that is likely to come to your mind is various species of fish. Understanding the life cycles habits habitats and inter-relationships of marine life contributes to our understanding of the planet as a whole. It is the largest and most diverse biome in the world.
Not only that but water provides a 3-dimensional habitat which increases the available habitat for the animals microbes and plants to live. Spongocoel- spacious cavity in sponge. Marine biology is the study of marine ecosystems marine organisms and human interactions with these environments and species.