Cellular Respiration Formula Explained

Cellular respiration helps cells break sugar which further helps in producing energy.
Cellular respiration formula explained. Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products. Process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as.
Such processes are explained below. Glucose oxygen chemical energy carbon dioxide water Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create atp a chemical which the cell uses for energy. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
This type of respiration is common in most of the. ENE1L5 EK ENE1L7 EK Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. A short video covering the topic of cellular respiration including the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration prepared for a year 9 science.
Adenosine triphosphate chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. Respiration is of two types aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in.
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is c6h1206 6o2 6co2 6h2o energy atp. Living active or occurring in the absence of free oxygen. During this activity the students work with a group to discuss the compounds and conditions that need to be present in order.
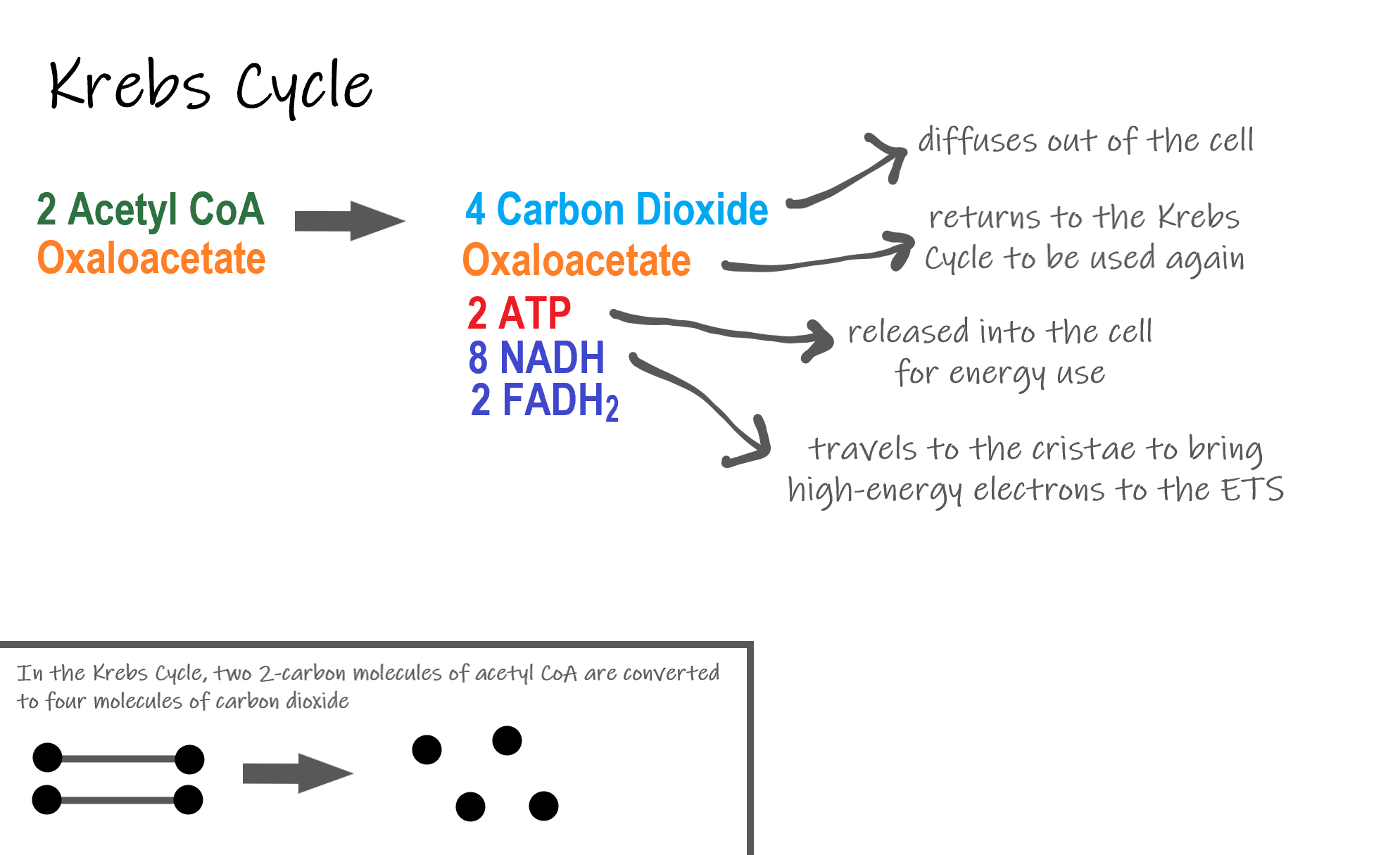
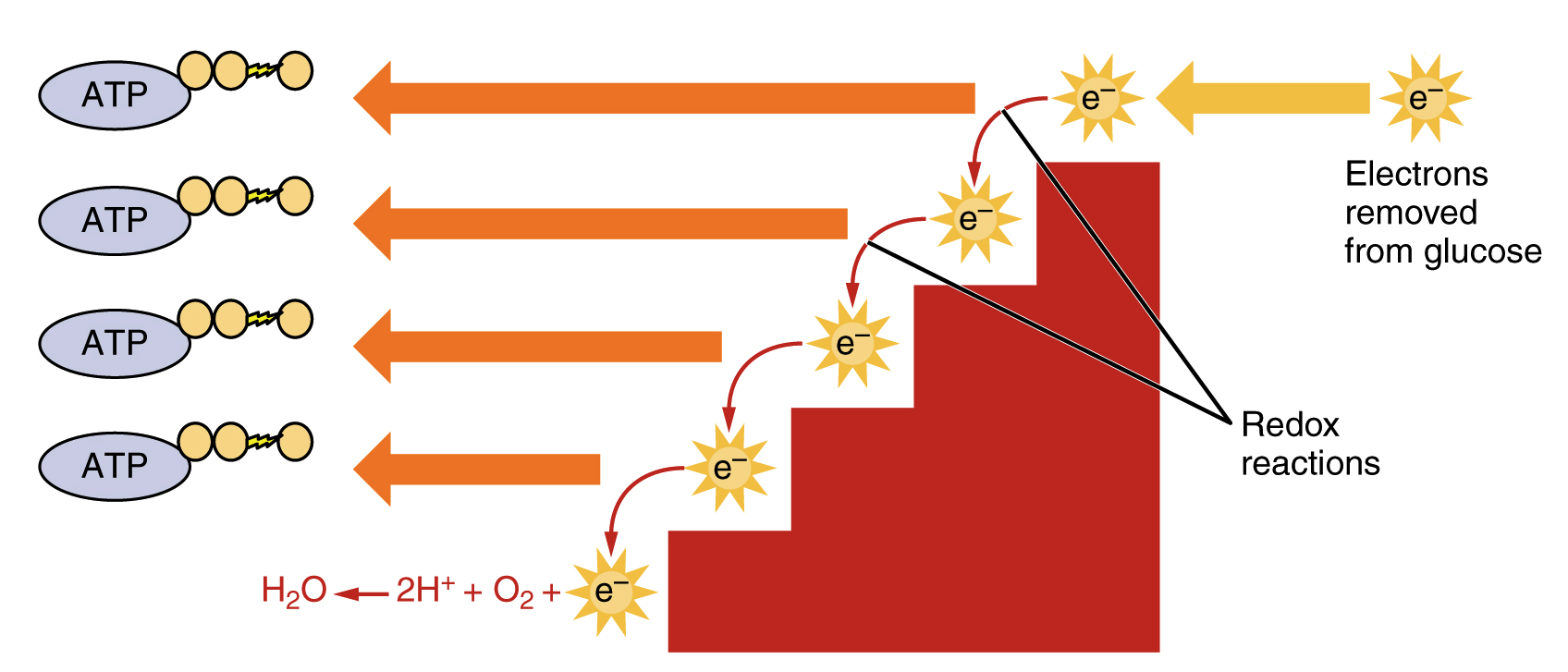
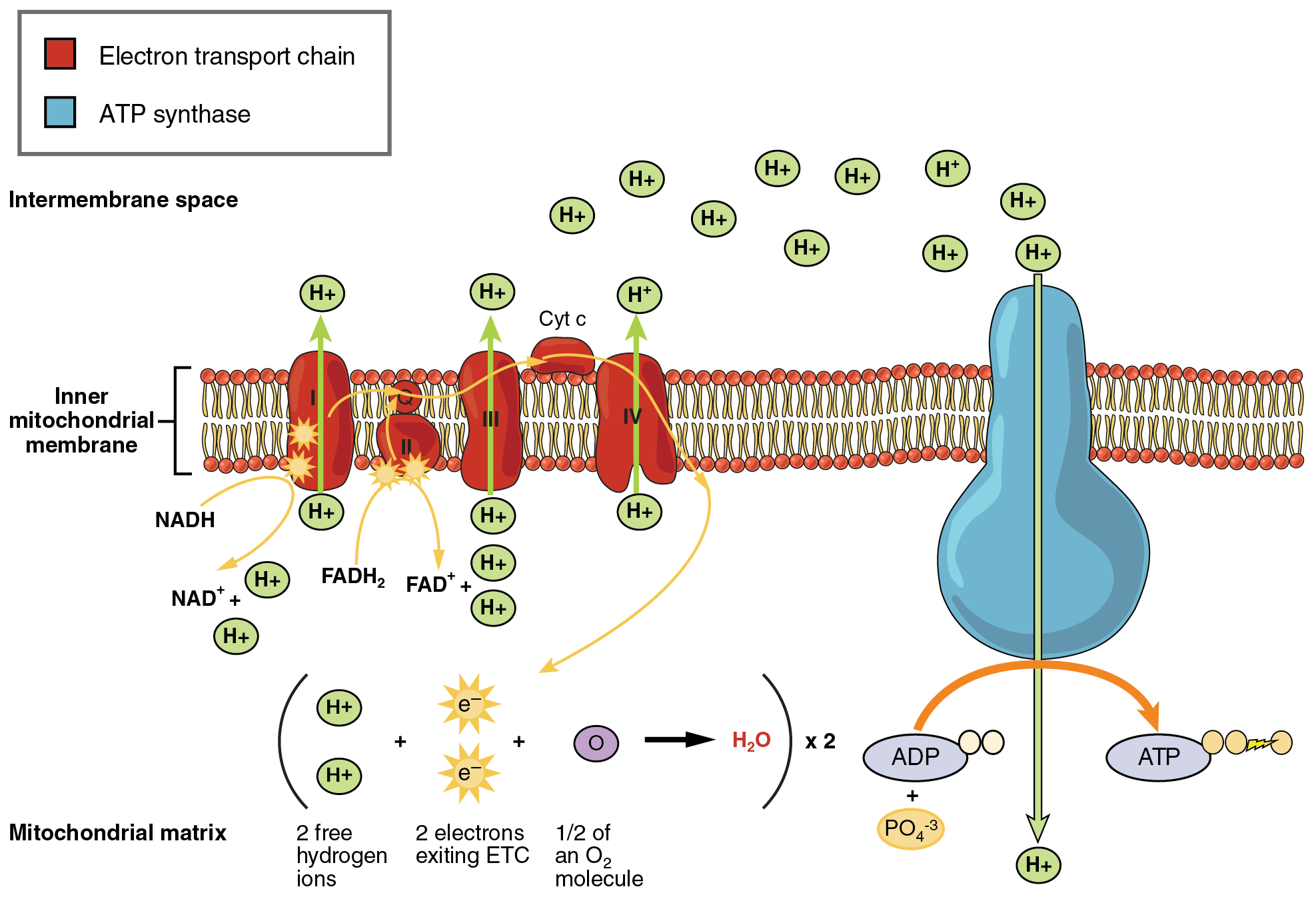
Cellular respiration is a common process that is carried out by many organisms to make and release energy. There are three main stages of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a process that is undergone in cells to break down molecules and produce ATP.