Cell Membrane Structure And Function Ppt

PowerPoint PPT presentation free to view.
Cell membrane structure and function ppt. The cell membrane is kind of like a soap bubble. JacksonChapter 7Membrane Structure andFunction Lectures by Erin Barley Kathleen Fitzpatrick 2011 Pearson Education Inc. Cell Structure and Function - Cell Structure and Function Central Vacuole Structure Large membrane bound sac Occupies the majority of the volume of the plant cell Increases cell s surface area.
Folded membrane within an outer membrane. Fluid pliableeasily moved - due to lipid component -phospholipids can move laterally b. Membranes also exist within cells forming various.
Osmosis is a kind of diffusion. The Structure and Function of the Cell Membrane PPT Notes Cells function similarly in all living organisms. Mosaic made of a combination of molecules lipids proteins and carbs Cell Membrane Animation Phospholipids Fatty acid.
The soapy membrane _____ the inside air from the outside. Cell organelles ppt - Google Slides. Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions The fluid mosaic model states that a membrane is a fluid structure with a mosaic of various proteins embedded in it.
Cell wall Great wall of China Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis Vacuole large central takes up most part of cell Cell membrane Regulates substances in and out of the cell. The structure and function of cellular organelles the cell is the smallest unit of life. Likewise the cell membrane is a thin flexible layer that seals the inside of.
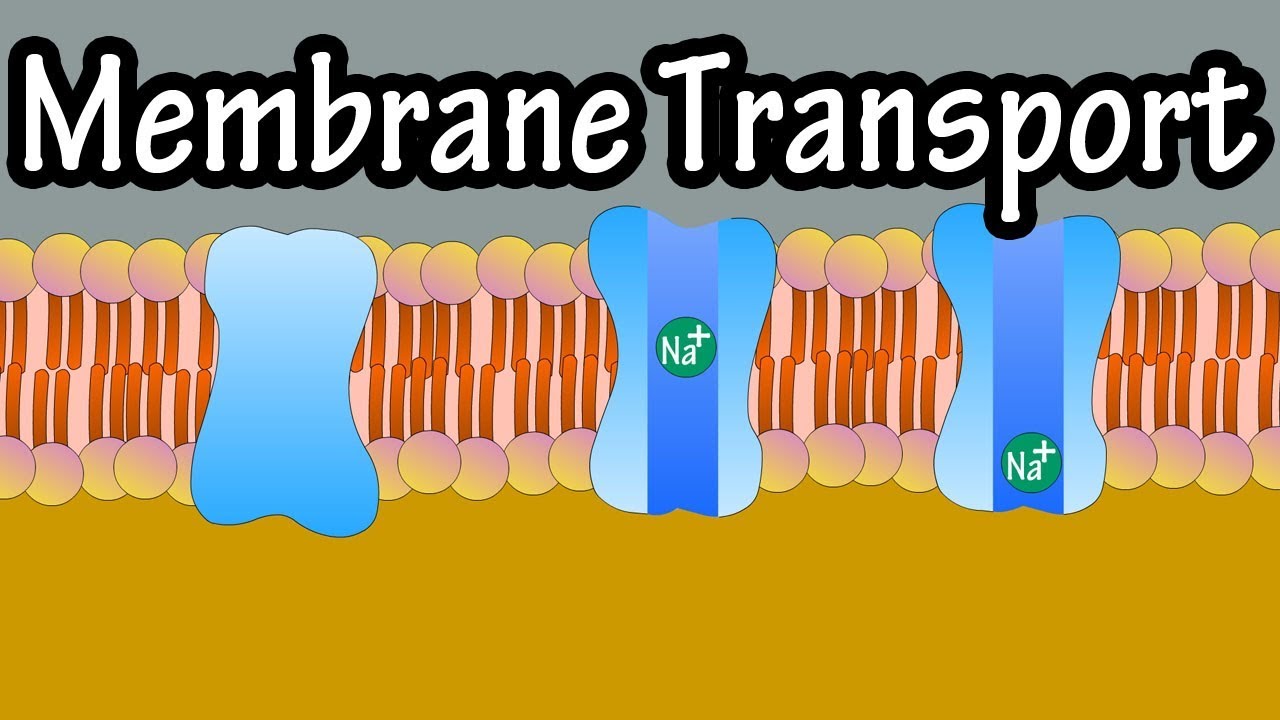
1 4 2 3 5. Functions of Membrane Proteins Can be peripheral or integral Ion channels allow flow of ions in and out of cell Carriers selectively move POLAR substances across membrane transporters Receptors specific to various molecules Ligand substance that binds to receptor Linkers help anchor cells together by bonding proteins or filaments together Cell-Identity Markers. The form and properties of the molecules determine their functions.